The first entry requires revenue accounts close to the IncomeSummary account. This means thatit is not an asset, liability, stockholders’ equity, revenue, orexpense account. Permanent accounts, such as asset, liability, and equity accounts, remain unaffected by closing entries. Closing entries are a fundamental part of accounting, essential for resetting temporary accounts and ensuring accurate financial records for the next period. This process highlights a company’s financial performance and position. In this guide, we delve into what closing entries are, including examples, the process of journalizing and posting them, and their significance in financial management.
What Is a Closing Entry?
- It’s necessary to properly assess depreciation for items like fixed assets and to amortize capitalized expenses as they each affect your balance sheet and taxable income.
- Examples of temporary accounts are the revenue, expense, and dividends paid accounts.
- Closing entries are performed after adjusting entries in the accounting cycle.
- At the end of the accounting period, the balances in these accounts are transferred to permanent accounts, resetting the temporary accounts to zero for the next period.
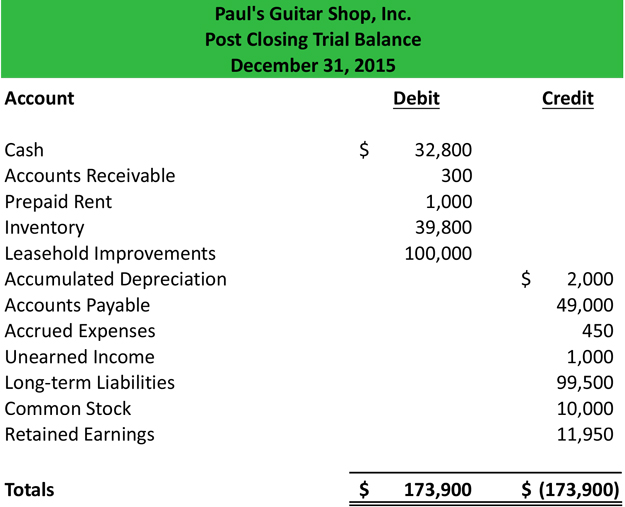
The trial balance shows the ending balances of all asset, liability and equity accounts remaining. The main change from an adjusted trial balance is revenues, expenses, and dividends are all zero and their balances have been rolled into retained earnings. We do not need to show accounts with zero balances on the trial balances. Accountants may perform the closing process monthly or annually.
Step 1 of 3
Temporary accounts are used to compile transactions that impact the profit or loss of a business during a year, while permanent accounts maintain an ongoing balance over time. Examples of temporary accounts are the revenue, expense, and dividends paid accounts. Any account listed in the balance sheet (except for dividends paid) is a permanent account. A temporary account accumulates balances for a single accounting period, whereas a permanent account stores balances over multiple periods. Temporary (nominal) accounts are accounts thatare closed at the end of each accounting period, and include incomestatement, dividends, and income summary accounts. This is no different from what will happen to a company at theend of an accounting period.
Step 1: Clear revenue to the income summary account
The year-end closing is the process of closing the books for the year. This involved reviewing, reconciling, and making sure that all of the details in the ledger add up. With the use of modern accounting software, this process often takes place automatically. Nigel Sapp is a content marketer at Numeric, partnering with top accountants to break down best practices, thorny accounting topics, and helping teams navigate the world of accounting tech. Like a well-oiled engine, a solid month-end close keeps your finances running smoothly and your business in the fast lane. Tasks like data entry, reconciliation, and reporting benefit greatly from automation tools, allowing your team to focus on more strategic activities.
If it all seems a bit complex or maybe you are a small business owner who takes on their own accounting, you may wonder if you really need to know closing entries in practice. The beautiful thing is that some accounting programs like QuickBooks, make these entries for you. Accounts can be closed on a monthly, quarterly, semi-annual or annual basis. It is really determined by a company’s need for financial reporting.
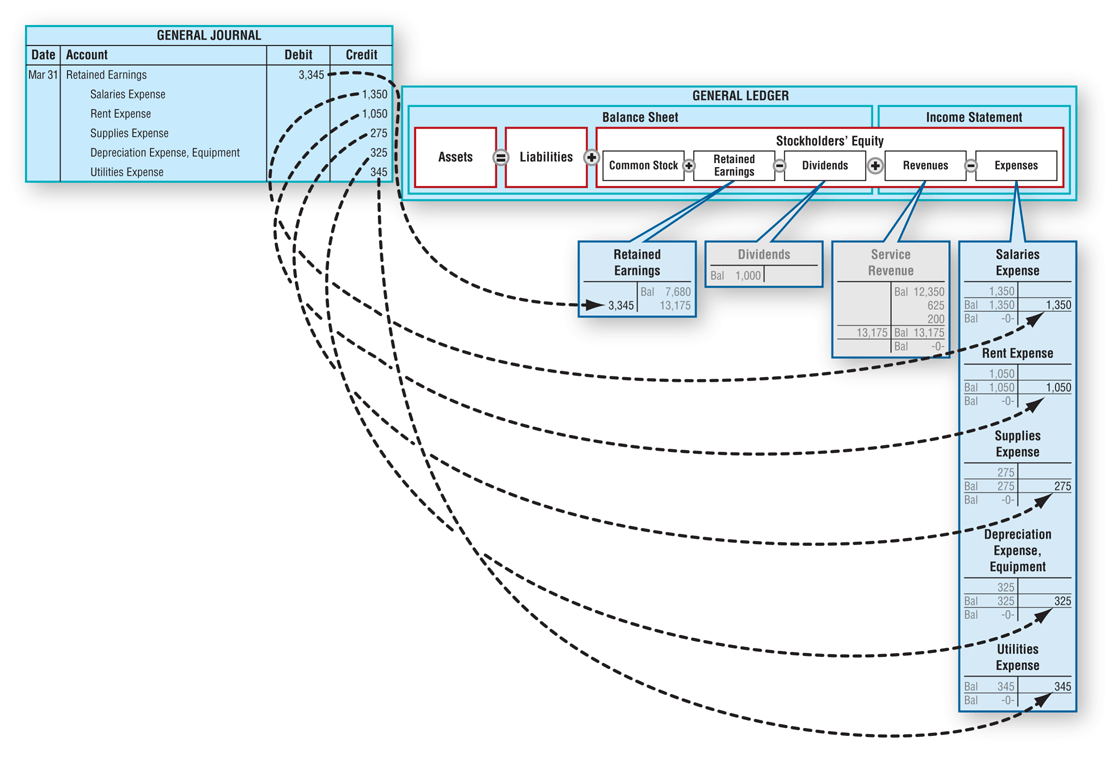
Close expense accounts
Adjusting entries are used to modify accounts so that they’re in compliance with the accrual concept of recording income and expenses. From the Deskera “Financial Year Closing” tab, you can easily choose the duration of your accounting closing period and the type of permanent account you’ll be closing your books to. Now, the income summary account has a zero balance, whereas net income for the year ended appears as an increase (or credit) of $14,750.
After preparing the closing entries above, Service Revenue will now be zero. The expense accounts and withdrawal account will now also be zero. Both closing and opening entries record transactions, but there is a slight variation in their purpose. Permanent what is the difference between notes payable and accounts payable accounts, also known as real accounts, do not require closing entries. Examples are cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and retained earnings. These accounts carry their ending balances into the next accounting period and are not reset to zero.
Without closing revenue accounts, you wouldn’t be able to compare how much your business earns each period because the amount would build up. And without closing expense accounts, you couldn’t compare your business expenses from period to period. On the statement of retained earnings, we reported the ending balance of retained earnings to be $15,190. We need to do the closing entries to make them match and zero out the temporary accounts. These entries are made to update retained earnings to reflect the results of operations and to eliminate the balances in the revenue and expense accounts, enabling them to be used again in a subsequent period.
